Taking Custom Design to New Levels
PROUD TO BE PART OF THE BRIN FAMILY OF COMPANIES

OTHER BRIN LOCATIONS
Brin Glass Company | Minneapolis, MN
St. Germain’s Glass | Duluth, MN
Heartland Glass | Waite Park, MN
As we navigate through 2023, the realm of humanoid robots continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, capturing the imagination of both the public and the industry. According to a report by Fortune Business Insights, the global humanoid robot market is projected to grow significantly, reaching USD 4.5 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 45.6%. This shift is driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics, positioning humanoid robots not just as technological marvels but as practical solutions in various sectors including healthcare, manufacturing, and customer service.
Understanding humanoid robots is paramount for grasping their role in modern society. These robots are designed to mimic human appearance and behavior, serving to enhance interactions in environments that demand personal engagement. As highlighted in studies from the International Federation of Robotics, integrating humanoid robots can improve productivity and efficiency in workplaces, while also providing companionship and assistance in domestic settings. This growing accessibility and functionality heralds a new age where humanoid robots can be seamlessly integrated into daily life, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of their capabilities and implications.

Humanoid robots in 2023 exhibit a range of key characteristics that enhance their functionality and human interaction. One of the most essential traits is their advanced mobility and dexterity, allowing them to mimic human movements with remarkable precision. This biomechanical design enables humanoid robots to navigate complex environments, perform tasks that require fine motor skills, and participate actively in daily activities alongside humans. Enhanced sensors and artificial intelligence algorithms also contribute to their ability to process environmental information and respond appropriately, which is crucial for tasks that demand real-time decision-making.
Another significant characteristic is their social and emotional intelligence. In 2023, many humanoid robots are equipped with sophisticated AI that allows them to recognize and interpret human emotions. This capability facilitates more natural interactions, as these robots can adjust their behavior based on the emotional state of the individuals they encounter. Furthermore, advancements in natural language processing enable humanoid robots to engage in meaningful conversations, making them more relatable and effective in roles such as caregivers, companions, or customer service representatives. Together, these characteristics not only enhance the utility of humanoid robots but also pave the way for deeper connections between humans and machines.
In 2023, advancements in humanoid robot technology have reached unprecedented levels, significantly enhancing their functionality and versatility. These robots are now equipped with advanced artificial intelligence, enabling them to understand and respond to human emotions and social cues more effectively. Enhanced machine learning algorithms allow these humanoid robots to learn from their interactions, adapting their behavior and responses over time to better meet the needs of their users. This evolution not only improves their utility in various applications, from personal assistance to customer service, but also fosters a more natural interaction between humans and machines.
Moreover, the integration of robotics with cutting-edge sensors and actuators has led to more fluid and lifelike movements. Humanoid robots can now replicate a wider range of human expressions and gestures, making them more relatable and approachable in social contexts. This breakthrough in mobility and expressiveness is further complemented by advances in power efficiency, enabling these robots to operate for longer periods without interruptions. As we continue to explore the potential of humanoid robotics, the focus on creating empathetic, versatile, and engaging machines could redefine human-robot interaction, opening new pathways for collaboration in everyday life.
| Feature | Description | Current Trends | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mimicry of Human Movement | Advanced sensors and actuators allow humanoid robots to closely mimic human movements. | Integration of AI for smoother interactions. | Healthcare assistance, therapy. |
| Facial Recognition | Utilizes AI algorithms to recognize human faces and process emotional responses. | Increased accuracy and speed in recognition processes. | Security systems, personalized customer service. |
| Machine Learning | Humanoid robots learn from experiences and improve interactions over time. | Applying reinforcement learning techniques. | Education, customer engagement. |
| Natural Language Processing | Enables robots to understand and respond to human speech. | Improving contextual understanding in conversations. | Virtual assistants, educational tools. |
| Physical Appearance | Designs that resemble humans closely enhance relatability. | Use of advanced materials for realistic features. | Companionship, promotional appearances. |
| Mobility | Humanoid robots are designed to navigate various environments. | Enhancements in stability and adaptability. | Logistics, exploration. |
| Emotional Intelligence | Capable of recognizing and responding appropriately to human emotions. | Focus on improving empathetic responses. | Mental health support, customer interactions. |
| Safety Features | Integration of sensors to prevent accidents and ensure user safety. | Real-time monitoring and adaptive interventions. | Elderly care, domestic environments. |
| Energy Efficiency | Development of low-energy consuming components for longer operation time. | Innovations in battery technology. | Mobile robots, service robots. |
| Interconnectivity | Ability to communicate with other devices and systems. | Increased integration with IoT. | Smart homes, industrial automation. |
Human-robot interaction (HRI) is an increasingly important area of study as humanoid robots become more integrated into various aspects of daily life. The relationship between humans and robots is complex, influenced by social norms, emotional responses, and the capabilities of the robots themselves. One of the primary challenges in HRI is ensuring that robots can interpret and respond to human emotions effectively. This requires advanced programming and machine learning techniques that can analyze non-verbal cues such as facial expressions and body language.
To enhance understanding in this realm, here are some essential tips. First, focus on empathy when designing humanoid robots. Empathetic responses can significantly improve user experience, making interactions feel more natural and engaging. Second, prioritize adaptability. A robot that can learn from interactions with its environment and improve over time will be more effective in real-world applications. Lastly, consider the ethical implications of HRI. Developers should address questions about autonomy, privacy, and data security, as these factors can influence public perception and acceptance of humanoid robots.
As we delve deeper into 2023, the ongoing evolution of HRI will likely unveil additional complexities, with researchers and engineers striving to create robots that not only function effectively but also resonate with users on a human level.
Humanoid robots have rapidly gained traction across various industries, showcasing their versatility and capability in performing tasks that align closely with human interaction. In healthcare, these robots are being employed as companions for the elderly, providing not only assistance but also emotional support. Their ability to understand and respond to human emotions enhances patient care and improves quality of life. Additionally, they are used in rehabilitation settings, offering physical assistance and motivation to patients recovering from injuries.
In the education sector, humanoid robots serve as engaging teaching assistants, facilitating interactive learning experiences for students. With their ability to communicate in multiple languages and respond to questions, they provide personalized instruction that can adjust to the needs of individual learners. Moreover, in the service industry, humanoid robots are being utilized in roles such as receptionists or guides, enhancing customer interaction with an innovative touch. This trend is creating new avenues for business efficiency and customer engagement, demonstrating the impactful integration of humanoid robots in everyday operations.
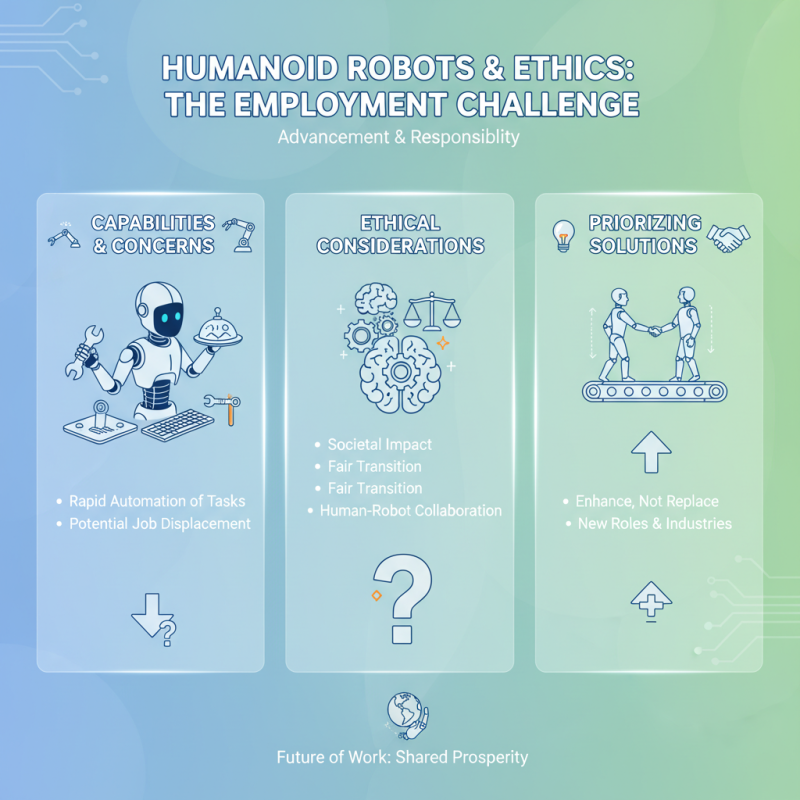
As humanoid robots continue to advance rapidly in their capabilities and applications, ethical considerations in their development have become increasingly critical. One of the foremost issues is the potential impact on employment. As robots become more adept at tasks traditionally performed by humans, there is a growing concern that widespread adoption could lead to significant job displacement. Developers must navigate this complex landscape by considering the societal implications of their innovations and prioritizing the creation of robots that enhance human work rather than replace it.
Another pressing ethical concern revolves around the idea of autonomy and decision-making in humanoid robots. As these robots are equipped with artificial intelligence, they may eventually be faced with moral dilemmas that require them to make decisions that could affect human lives. It is essential for developers to establish clear ethical guidelines and frameworks that govern how these robots operate and interact with humans. Transparency in the algorithms and decision-making processes of humanoid robots is necessary to build trust and ensure accountability in their use, particularly in sensitive sectors such as healthcare and security. By addressing these ethical considerations, developers can contribute to a future where humanoid robots serve as beneficial partners in human society.





Taking Custom Design to New Levels

Brin Glass Company | Minneapolis, MN
St. Germain’s Glass | Duluth, MN
Heartland Glass | Waite Park, MN

Fabricator
Inside Sales and Client Support Manager
Glass Handler – 1st Shift